CONDUCTION AND CONVECTION
Section outline
-
Welcome to the Conduction and Convection course! This course is designed to guide you through the fascinating principles of heat transfer, focusing on two primary mechanisms: conduction and convection. You'll explore how thermal energy moves through solids, liquids, and gases, gaining a deep understanding of the scientific and practical applications of these processes. From analyzing material properties to studying fluid dynamics, this course combines theoretical knowledge with real-world examples. Whether you're new to the subject or looking to enhance your expertise, you'll find this course both engaging and insightful. Let’s embark on this exciting journey of discovery together!
Objective of the Conduction and Convection Course:
The primary objective of this course is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the principles and mechanisms of heat transfer through conduction and convection. By the end of the course, students will be able to:
Understand Fundamental Concepts: Grasp the basic principles of heat transfer, including thermal conductivity, heat flux, and temperature gradients in conduction, as well as the dynamics of fluid flow in convection.
Analyze Heat Transfer Mechanisms: Apply mathematical models and equations, such as Fourier’s law for conduction and Newton’s law of cooling for convection, to solve practical heat transfer problems.
Explore Material Properties and Applications: Investigate how material properties and fluid dynamics influence heat transfer, with applications in engineering, environmental science, and industry.
This course is tailored to equip students with both theoretical knowledge and practical insights for careers in engineering, research, and applied sciences.
-
This course has provided an in-depth understanding of heat transfer mechanisms, including conduction, convection, and radiation. Key takeaways include:
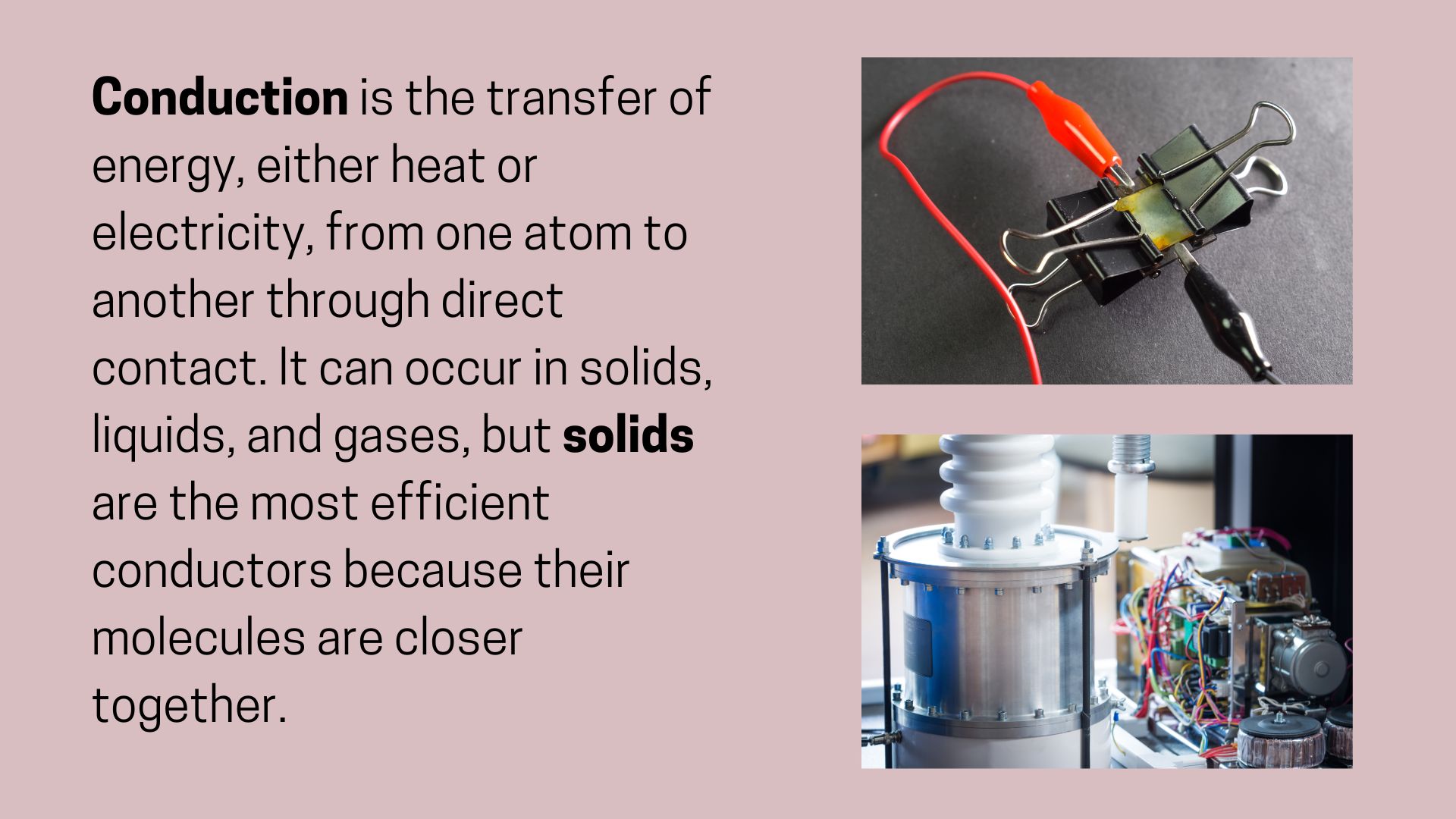
Conduction:- The transfer of energy through a material, driven by particle interactions, was explored using Fourier’s Law. Practical applications such as calculating heat loss through materials demonstrated the importance of thermal conductivity in engineering design and material selection.
- The study of heat transfer between a surface and an adjacent fluid in motion emphasized Newton's Law of Cooling. The significance of convection coefficients, fluid properties, and flow conditions in heat exchange systems was highlighted
- Real-world scenarios, such as calculating heat loss in buildings and designing efficient heating systems, showed how heat transfer principles apply to energy conservation and system efficiency.
REFERENCE:
Incropera, F. P., & DeWitt, D. P. (2011). Fundamentals of heat and mass transfer (7th ed.). Wiley.
Çengel, Y. A., & Ghajar, A. J. (2020). Heat and mass transfer: Fundamentals and applications (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
Holman, J. P. (2010). Heat transfer (10th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
Lienhard, J. H., & Lienhard, J. H. V. (2019). A heat transfer textbook (5th ed.). Phlogiston Press.
Özışık, M. N. (1993). Heat conduction (2nd ed.). Wiley.