Strong Base
Section outline
-
-
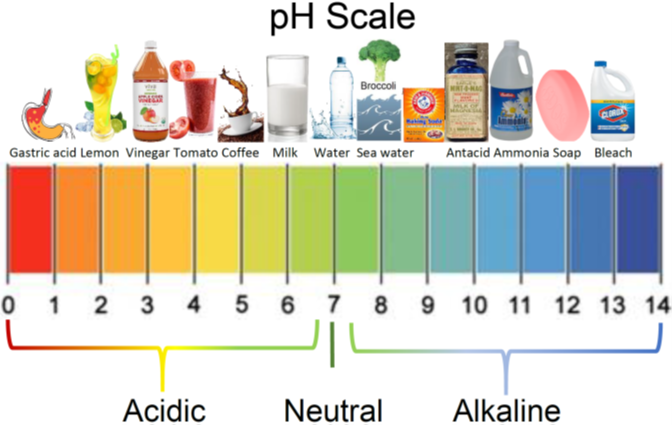
Definition: Strong bases completely dissociate in water, releasing a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻). This makes the solution highly alkaline.
-
Characteristics:
-
Fully ionized in aqueous solutions.
-
High pH, typically above 12 for concentrated solutions.
-
Very effective at neutralizing acids.
-
-
Examples:
-
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
-
Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
-
Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂)
-
-
Reaction Example:
-