NON-EDIBLE OIL AND FAT PRODUCT FROM USED COOKING OIL (UCO)
Section outline
-
-
Please feel free to introduce yourself here!
-
-
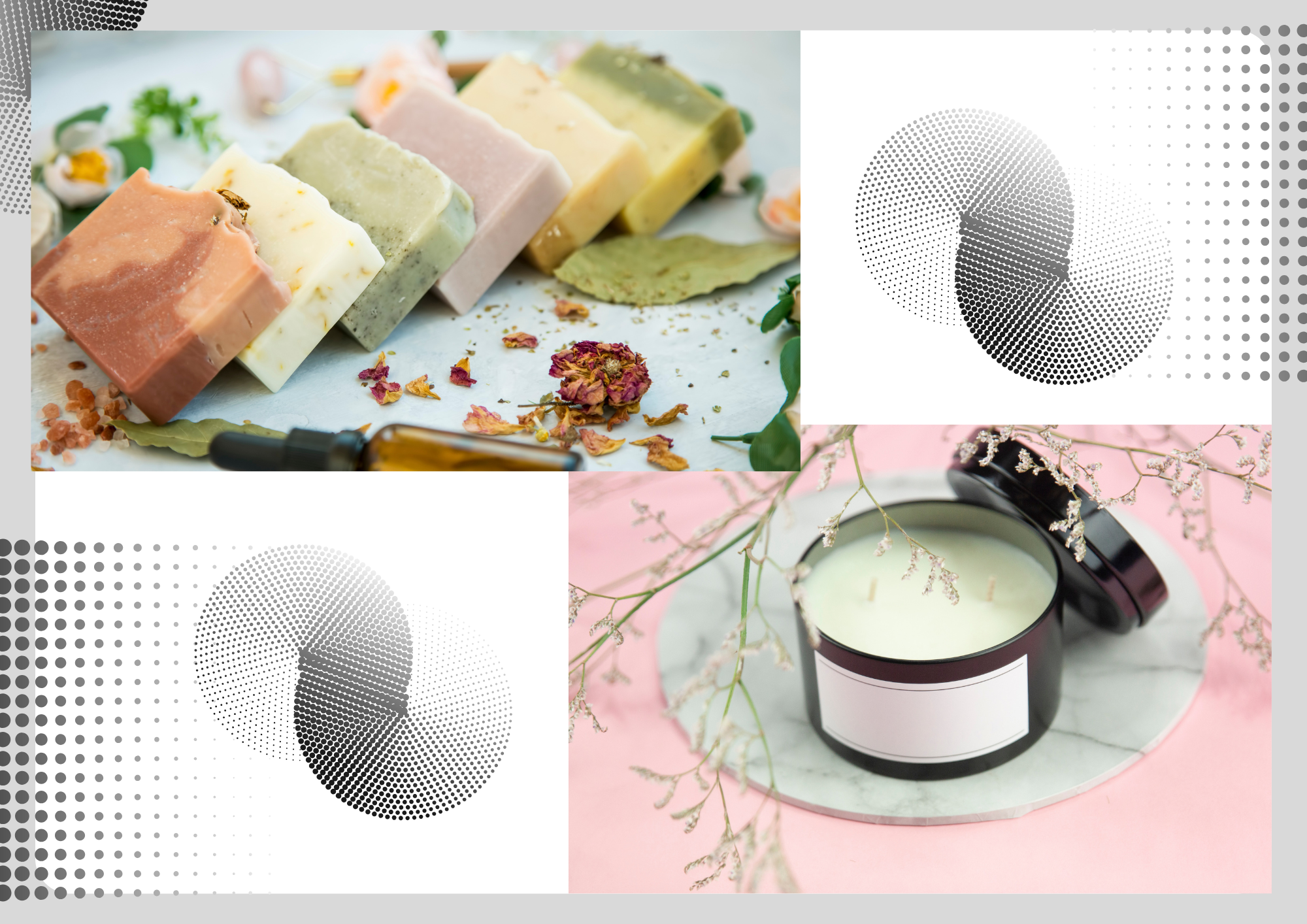
This module introduces learners to the sustainable conversion of used cooking oil (UCO) into non-edible value-added products. Students will first explore the characteristics and chemical behavior of used cooking oil, including the changes that occur during repeated heating and the environmental issues caused by improper disposal. Building on this understanding, learners will then be guided through two practical applications: the production of soap using the cold-process saponification method, and the production of scented candles using UCO as a base material. Each section is designed to provide foundational theory, essential calculations, identification of materials, and hands-on procedures. By the end of this module, students will gain both conceptual understanding and practical skills related to waste valorization and simple product formulation.

-
LEARNING OUTCOMES
- Students will be able to differentiate the environmental impacts caused by improper disposal of used cooking oil
- Students will be able to demonstrate the cold-process method of soap production using filtered used cooking oil
- Students will be able to construct a basic scented candle using used cooking oil following proper safety procedures
-
-
LEARNING OUTCOME
Students will be able to explain the chemical composition of used cooking oil and how repeated heating affects its quality.
-
-
LEARNING OUTCOME
Students will be able to explain the chemical principles of saponification, lye calculation (NaOH) and SAP Index -
Discuss about Topic 2.
-
-
LEARNING OUTCOME
Students will be able to define the primary components of a scented candle (wax, wick, fragrance), Used Cooking Oil (UCO) as a triglyceride and explain the physical limitations that prevent its use as a 100% candle wax replacement. -
Discuss about Topic 3.
-
In summary, this learning module highlights how used cooking oil often viewed as waste, can be transformed into useful non-edible products through simple chemical processes. Students have learned the composition and environmental impact of UCO, the principles of saponification and lye calculation for soap making, and the essential materials and steps involved in producing scented candles. These topics demonstrate the importance of sustainable practices, resource recovery, and basic formulation techniques. Ultimately, learners should be able to appreciate how small-scale waste-to-product innovations contribute to environmental conservation while providing practical skills that can be applied in daily life or introductory laboratory settings.
-
Please drop a feedback.
-