MAINTENANCE ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT IN MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY
Section outline
-
Maintenance Engineering and Management in Manufacturing Industry
-
Course Synopsis
Maintenance Engineering and Management in Manufacturing Industry
Welcome to the “Maintenance Engineering and Management in Manufacturing Industry” course! This course provides a comprehensive introduction to the principles, strategies, and best practices of maintenance engineering within modern manufacturing environments. It is designed for students who wish to develop essential knowledge and practical understanding of how effective maintenance contributes to productivity, reliability, and cost efficiency.
Over the duration of the course, participants will:
-
Learn the fundamental concepts of maintenance engineering and the importance of maintenance management in manufacturing operations.
-
Understand different types of maintenance strategies such as preventive, predictive, and corrective maintenance.
-
Gain insights into maintenance planning, scheduling, and resource management to improve equipment performance and lifespan.
-
Explore modern technologies used in maintenance management, including condition monitoring, Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), and Industry 4.0 applications.
-
Analyze case studies and real-world examples to identify best practices and solutions to maintenance-related challenges.
-
Develop teamwork and problem-solving skills through practical assignments and project-based learning.
-
-
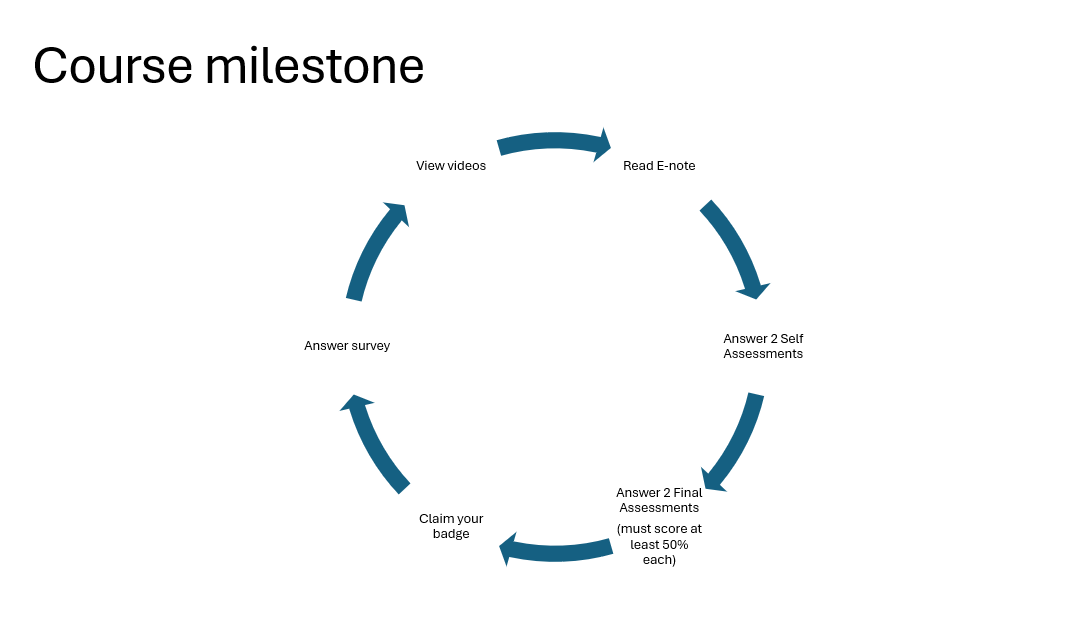
Students are required to complete two assessments at the end of the course and achieve a minimum score of 50% to pass.
By the end of this course, participants will possess the foundational knowledge and practical understanding needed for entry-level roles in maintenance, production, or manufacturing management — serving as a strong platform for further specialization or career advancement in the engineering field.
Join us to explore how effective maintenance engineering and management can drive performance, reliability, and sustainability in today’s manufacturing industry!
-
-
INTRODUCTION
-
INTRODUCTION
Manufacturing has played a crucial role in human civilization, transitioning from handcrafted products to the highly automated procedures that characterize modern manufacturing. Innovations in technology have greatly increased production, efficiency, and quality since the Industrial Revolution. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are one example of this innovation, which has transformed industry by making automated and extremely accurate machining possible. CNC machines reduce human error and increase production consistency by using pre-programmed software to operate tools and equipment. Because these machines can perform complicated cutting, drilling, milling, and turning operations with great accuracy and efficiency, they are extensively utilized in sectors including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and manufacturing of metals. CNC technology, combined with advancements like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), is transforming manufacturing through increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved product quality. Even with these developments, maintenance is still necessary to guarantee the effective and reliable operation of production machines, especially CNC machines.
In manufacturing, maintenance can be divided into four main categories: predictive maintenance, which uses data and monitoring systems to predict possible problems before they occur; corrective maintenance, which fixes minor issues before they become major failures; breakdown maintenance, which deals with sudden equipment failures that require immediate repairs; and preventive maintenance, which involves periodic checks and servicing to avoid unexpected failures. Preventive maintenance in CNC machining involves inspecting cutting tools to stop wear and tear, lubricating moving parts, and cleaning machine components. IoT sensors may be used for predictive maintenance, which tracks machine performance, identifies deviations, and plans repairs before breakdowns happen. These tactics not only increase the lifespan of equipment but also improve operational effectiveness and decrease production downtime.
Basic maintenance is important for maintaining worker safety and production efficiency. IoT sensors, for example, are used in predictive maintenance in the automobile sector to track engine performance and identify any problems before they affect output. Preventive maintenance keeps food processing equipment hygienic and operational in order to meet hygienic standards. Corrective maintenance takes care of little defects in electronics production before they cause large losses in product value. For accuracy and consistency, CNC machines in the metal fabrication industry need to have their calibration and tool replacements done on a regular basis. By putting these maintenance techniques into practice, producers may minimize downtime, uphold high standards of quality, and maximize overall production efficiency, providing reliable and effortless operations.
The chart below shows the organizational chart in the industry. The manufacturing industry's organizational structure is crucial for good coordination, output, and efficiency. Production managers are responsible for monitoring operations, manufacturing engineers optimize processes, and quality control specialists guarantee product standards. Supply chain managers manage logistics, maintenance technicians keep up with machinery, and machine operators operate machines. Ensuring the industrial facility operates in a productive and efficient manner is the duty of maintenance management (Mobley, 2002). A well-designed system minimizes downtime, improves quality, and guarantees safety; a neglected system causes delays, breakdowns of equipment, and more costs. To maintain industrial efficiency and competitiveness, effective organization is important.
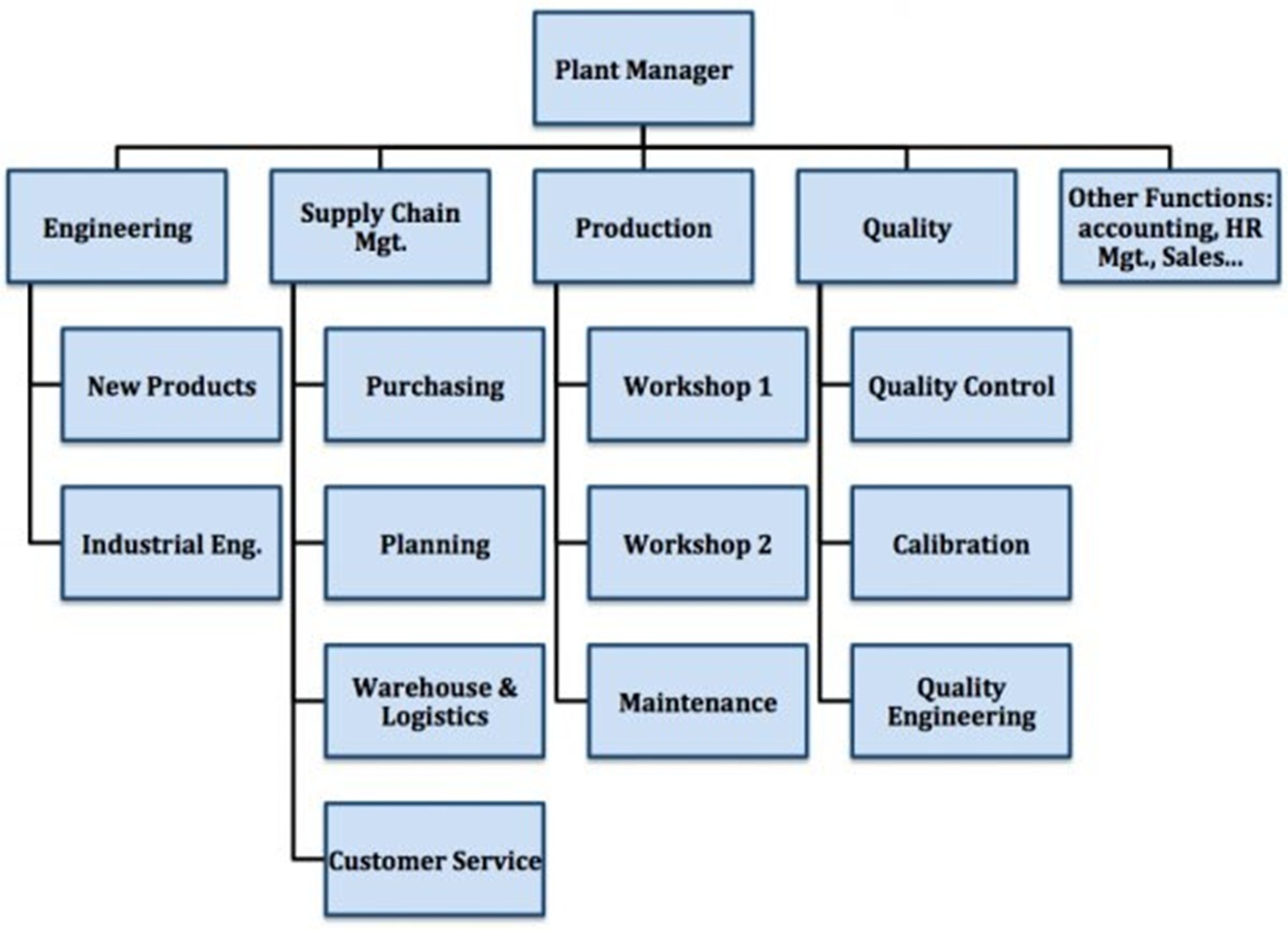
Figure 1: Organization Chart
The manufacturing system shown in the illustration below follows a systematic CNC machining procedure to guarantee accuracy, effectiveness, and quality. Finding specific raw materials appropriate for production occurs after an analysis meeting to go over project requirements. Then, to manage machining processes, CNC software is created. After that, the right cutting tools are made, and automatic tool changes will be set in place. High-precision machining is done at the CNC processing step, and accuracy is verified by inspecting the CNC components. After surface treatment improves finishing and durability, the finished items are ultimately packed for shipping. In modern industrial applications, this systematic strategy optimizes production efficiency, quality control, and resource use by integrating new manufacturing processes.

Figure 2: Structured CNC Machining Process in Manufacturing Industry
-
-
-
-
EFFECTIVE MANUFACTURING SCHEDULING FOR CNC MAINTENANCE AND PRODUCTIVITY
In order to guarantee effective coordination of production and maintenance, manufacturing scheduling is required. So as to reduce downtime and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), manufacturers should plan maintenance tasks, schedule production operations, and manage resources as efficiently as possible. While ensuring that production goals are achieved, essential scheduling techniques like job order scheduling and machine loading allow for the effortless integration of maintenance tasks. Furthermore, by enhancing work priority and resource management, Critical Path Method (CPM) software reduces the possibility of delays and equipment breakdowns.
In CNC machine maintenance Effective scheduling is important for preserving high performance levels and ensuring machine durability in CNC machine maintenance. Predictive maintenance strategies, which leverage data analytics and condition monitoring, allow manufacturers to detect potential issues before failures occur (Smith & Brown, 2021). CNC machines operate more effectively, and maintenance is reduced when predictive maintenance is integrated into scheduling. Moreover, structured scheduling improves CNC machine reliability by aligning preventive maintenance activities with low-production periods, reducing operational disruptions, and enhancing overall productivity (Jones et al., 2020).
An effective demand forecast, resource availability, and adaptability to unexpected developments are required for a successful production schedule. To guarantee that equipment is maintained without affecting productivity, it must match production objectives with maintenance requirements. By including predictive and preventive maintenance in the schedule, unexpected equipment failures may be avoided, which lowers downtime and improves productivity. To avoid delays and lack of resources, manufacturing, maintenance, and inventory teams must communicate clearly with one another. Furthermore, producers may make flexible schedule adjustments through real-time monitoring and data-driven decision making, which improves overall operational efficiency and provides efficient production procedures.
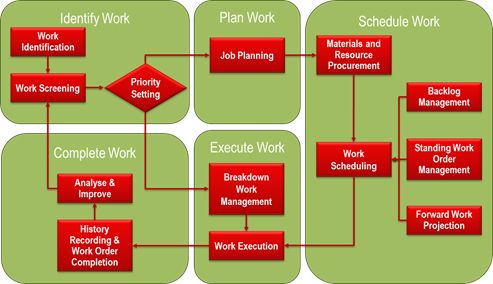
Maintenance of Scheduling
-
-
Job description of Maintenance Engineer - Roles, Responsibilities & Skills
-
-
Answer all questions
-
-
EFFECTIVE MANUFACTURING SCHEDULING
-
COMPUTERIZED MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (CMMS)
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) are required to increase the industrial sector's maintenance efficiency. By automating work order management, inventory monitoring, and maintenance scheduling, CMMS makes sure that equipment continues to remain in top shape. CMMS helps decrease unexpected breakdowns, eliminate downtime, and increase the lifespan of equipment by combining predictive and preventative maintenance techniques. Furthermore, capabilities like real-time reporting, safety tracking, and inventory management improve operational efficiency by enabling manufacturers to optimize maintenance procedures and make data-driven choices.
CMMS is essential for preserving quality and machine reliability in CNC machining. Since CNC machines need to operate with high precision and reliability, CMMS supports tracking maintenance tasks, maintaining updates on wear patterns, and scheduling preventative maintenance using real-time data. In order to identify possible faults before they occur, CMMS incorporates predictive maintenance techniques, including vibration analysis and heat monitoring. Furthermore, CMMS promotes the management of spare parts, minimizes human error, and provides that maintenance procedures are not interfering with output. Cloud services, IoT sensors, and CMMS improve CNC machine efficiency, reduce expenses, and increase production output as manufacturing moves toward Industry 4.0.

CMMS for Manufacturing Industry.
-
Equipment Maintenance Management.
-
-
-
CONCLUSION
-
CONCLUSION
In the manufacturing industry, effective operations depend on efficient maintenance management, especially when using CNC machining. A structured CNC machining procedure ensures accuracy, productivity, and reliability in output. This covers machining, programming, tooling setup, design, and quality control. From conventional techniques to more modern techniques like Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), maintenance strategies have changed over time. These techniques, which include preventive, predictive, and proactive maintenance, support maximizing production efficiency and minimizing downtime. Through the integration of regular maintenance, real-time monitoring, and data-driven decision-making, manufacturers may increase equipment lifespan, save costs, and improve quality. By implementing TPM concepts like autonomous maintenance and continuous improvement, long-term performance is ensured by developing a collaborative and responsible society.
In order to improve automation and predictive analytics, maintenance management advancements depend on AI, machine learning, and IoT. Real-time monitoring, less handling, and equipment breakdown prediction are all made possible by these advancements, which increase maintenance efficiency. Manufacturers need to adopt new maintenance techniques and digital transformation to stay competitive. Property tracking, work order automation, and preventative maintenance scheduling are all made easier with Fiix CMMS, a top cloud-based maintenance tool. Organizations may minimize unexpected breakdowns by connecting Fiix CMMS with IoT devices, which gives them immediate insight into equipment power. Fiix CMMS's AI-driven analytics facilitate data-driven decision-making, which improves resource allocation and maintenance procedures. Long-term company sustainability, operational productivity, and equipment performance are all improved by putting intelligent maintenance systems like Fiix CMMS into practice.
Advanced CMMS technology and organized CNC machines significantly improve production performance. Providing resources and managing resources are optimized through the strategic use of Fiix CMMS. Manufacturers may increase productivity and competitiveness through digitalization and proactive maintenance techniques. Organizations may improve flexibility and resilience in an industry that is changing quickly by integrating CNC machining, IoT, AI-driven analytics, and CMMS software. These connections increase machine uptime and overall production in addition to reducing maintenance. Modern maintenance techniques will help companies succeed in the future as competition grows. Reliability, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability are ensured by implementing CMMS software and organized machining procedures, setting up companies for future growth in a manufacturing environment that is always changing.

Fiix Software
REFERENCES
Mobley, R. K. (2002). Maintenance engineering handbook. McGraw-Hill Professional.
Mishra, R.C. (2005). Reliability and Maintenance Engineering, New Age International Publishers, New Delhi.
Nakajima, S. (1988). Introduction to Total Productive Maintenance (TPM). Productivity Press.
Smith, R., & Mobley, K. (2008). Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability Engineers.
Smith, J., & Brown, R. (2021). Advanced Manufacturing Scheduling Strategies. Industrial Press.
Jones, P., Taylor, M., & White, L. (2020). Predictive Maintenance in Smart Manufacturing. Springer.
-
-